Laravel supervisor configuration - process queued jobs in production
Oct 14, 2023
In software engineering, a queue offers an efficient solution for handling time-intensive tasks, such as processing file uploads, invoking third-party APIs, and bulk database uploads. Queuing these tasks not only enhances user experience but also promotes cleaner code.
Laravel includes built-in support for queues and requires the use of the php artisan queue:work command for processing queued jobs. However, running queue:work command in a production environment can be unreliable, as some jobs may fail. To address this issue, Supervisor, a process monitoring tool for Unix-like environments (with potential workarounds for Windows), becomes crucial. With Supervisor, you can reliably run the queue:work process in production, even between program exits or system restarts.
This article provides a brief explanation of how to process queues in Laravel using Supervisor.
Prerequisite
- Linux environment
- Laravel project with queue already configured
Install Supervisor
sudo apt install supervisor
After the installation is completed, supervisor runs automatically.
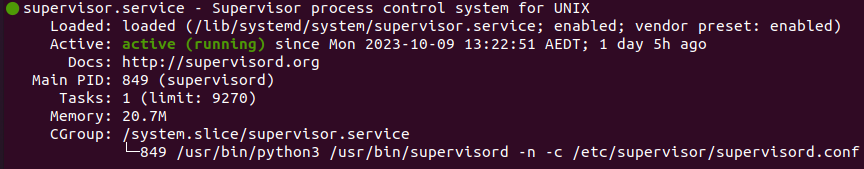
You can verify it by running sudo systemctl status supervisor command which returns output like below:
Configure queue worker in supervisor
Supervisor configuration files are located at /etc/supervisor/conf.d directory. You can cd into the directory and create queue-worker.conf file. A typical supervisor program that monitors laravel queue looks like below:
[program:queue-worker]process_name=%(program_name)s_%(process_num)02dcommand=php /absolute-path/to/project/artisan queue:work --sleep=3 --tries=3 --max-time=3600autostart=trueautorestart=truestopasgroup=truekillasgroup=trueuser=ubuntunumprocs=2redirect_stderr=truestdout_logfile=/path/to/project/storage/logs/supervisord.logstopwaitsecs=600
In the above configuration, supervisor will run 2 queue:work processes, watches and auto-restart them when they fail. According to Laravel docs, the value of stopwaitsecs should be greater than the time
taken by the longest running job. Lastly, command and user variables depend on your server configuration.
Run supervisor
After a new program is added, we need to inform supervisor to look for any new or updated program by running the following commands:
sudo supervisorctl reread
sudo supervisorctl updated
Finally start the queue worker by running below command:
sudo supervisorctl start queue-worker.conf